Cloud Migration Best Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic landscape of the digital era, businesses are rapidly transitioning to cloud computing, enticed by the promises of enhanced efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, to get to the cloud, organizations must migrate their applications, data, and IT resources from traditional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based environments.
The path to the cloud has some potential pitfalls that must be avoided. A successful cloud migration necessitates meticulous planning, strategic execution, and strict adherence to established best practices. These steps ensure that organizations not only maximize the potential benefits of the cloud but also minimize potential risks and disruptions that could compromise the migration process.
This article will delve into the intricacies of cloud migration, offering a comprehensive guide to fundamental best practices that pave the way for a seamless and successful transition. From understanding the cloud migration journey and its stages to exploring the role of tools and strategies in this process, we aim to provide actionable insights to inform and enhance your cloud migration initiatives.
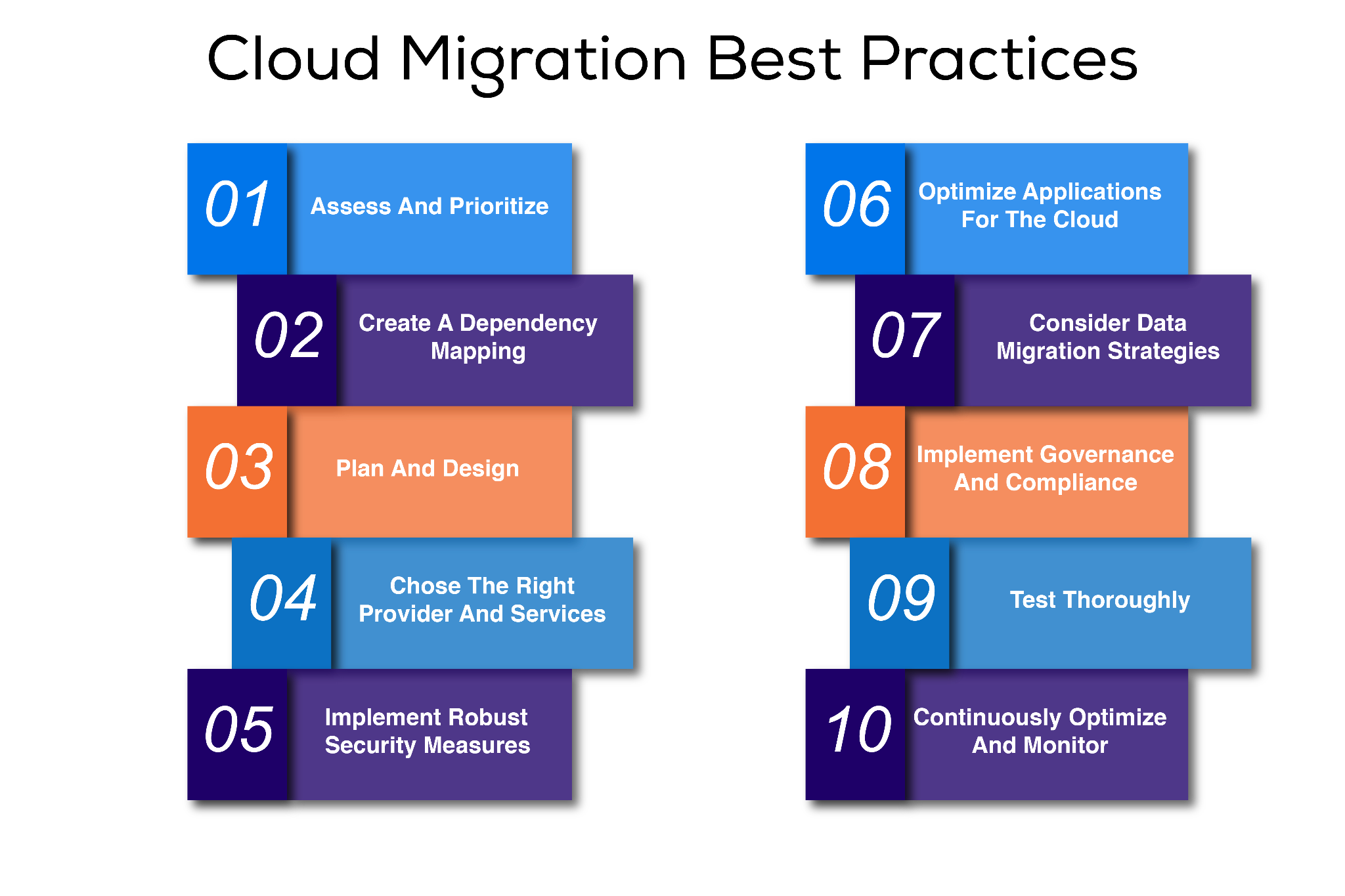
Summary of cloud migration best practices
| Best practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Assess and prioritize | Evaluate applications and workloads to determine their suitability for moving to the cloud. Prioritize workloads based on their complexity, dependencies, and business value. |
| Create a dependency mapping | Identify and understand the interdependencies among applications, servers, and other components within the IT infrastructure. |
| Plan and design | Develop a comprehensive migration plan, and design the target cloud architecture to ensure the best possible outcome from the migration process. This includes practices such as plan creation, establishing collaboration among stakeholders, and ensuring scalability, security, performance, and compliance. |
| Choose the right provider and services | Select the cloud provider that best matches both technical and organizational requirements. Take into account each provider’s track record, service offerings, resources, compatibility, security, compliance, pricing, and support. |
| Implement robust security measures | Implement data encryption in transit and at rest, strong access controls, multifactor authentication, and network security measures. |
| Optimize applications for the cloud | Rearchitect applications to leverage cloud-native services. For example, design for elasticity, scalability, serverless, and CDNs. |
| Assess data migration strategies | Look at strategies such as the following:
|
| Implement governance and compliance | Mitigate risks, maintain data integrity, and meet regulatory requirements by establishing robust governance and compliance frameworks in the cloud. |
| Test thoroughly | Perform thorough functional testing, data migration and storage process testing, and scalability and resilience testing to ensure a seamless migration process. |
| Continuously monitor and optimize | Long-term success requires constantly monitoring performance, alerts, analytics, and security to ensure the health and safety of the cloud implementation. Optimization is an essential, iterative process of assessment and improvement to enhance performance and adapt to relevant changes. |
Cloud migration best practices in detail
Successful execution of a cloud migration necessitates meticulous planning, strategic decision-making, and adherence to established best practices to ensure a smooth transition. Below, we describe ten suggested best practices.
Assess and prioritize
Assessing and prioritizing applications and servers for cloud migration involves evaluating the existing IT infrastructure, applications, and workloads to determine their suitability for migration and the potential specific benefits of moving them to the cloud.
Start by conducting a comprehensive assessment, considering business goals, technical requirements, and regulatory compliance. This assessment helps identify critical workloads and dependencies that need to be migrated.
Once the assessment is complete, prioritize the migration of workloads based on their strategic importance, complexity, and potential benefits. Consider factors such as cost savings, scalability, and improved performance. Start with the least critical functions to minimize business disruption and allow for fine-tuning of the migration process before tackling more essential workloads.
Create a roadmap that outlines the order in which workloads will be migrated, considering any interdependencies or potential risks. The organization can gain valuable insights and experience by starting with the least critical workloads, enabling the smoother migration of more mission-critical functions in subsequent phases. This iterative approach also facilitates continuous optimization and refinement of the migration plan based on lessons learned during the initial phases.
Organizations can leverage various tools and methods to assist in assessing and prioritizing. For example, cloud migration assessment tools, cloud readiness frameworks, and engagement with cloud service providers or consultants can provide valuable insights and expertise to support decision-making.
A configuration management database (CMDB) also helps with inventory and dependency mapping, impact analysis, and risk management. A CMDB enables organizations to understand their IT assets, applications, dependencies, and potential risks, facilitating effective planning, execution, and ongoing cloud migration management.
Create a dependency mapping
Dependency mapping is closely tied to cloud migration’s assessment and prioritization process. It involves identifying and understanding interdependencies within the IT infrastructure. Dependency mapping is crucial because migrating an application without considering its dependencies can lead to disruptions, performance issues, or even failures in the cloud environment.
Organizations identify the relationships and dependencies between applications, servers, and other IT resources when conducting dependency mapping for cloud migration. This information is used to create move groups, which are logical groupings of applications that share dependencies or have strong interdependencies with each other.
Move groups help determine the order in which applications or components should be migrated to the cloud. They also help mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and facilitate testing and validation activities based on the identified dependencies and interdependencies during the migration process.
To illustrate, let’s consider a scenario where host ABC utilizes NGINX and host XYZ employs MySQL. These configuration items (CIs) are interconnected to support a front-end and back-end application architecture. In this case, host ABC relies entirely on host XYZ, establishing a strong dependency between them. As a result, they must be placed within a move group to ensure that they are migrated together.

A basic CMDB application mapping of two hosts (ABC and XYZ) and the applications installed on them (NGINX and MySQL). (Source)
Device42’s business service mapping helps with automatically mapping infrastructure to applications. It can create an affinity group that contains a SQL server and web server front-end, for example. This process is essential to creating the prioritization and migration schedule and reducing the risks associated with migration.
Plan and design
Developing a comprehensive migration plan and designing the target cloud architecture are crucial elements of a successful and efficient migration process. These practices require careful planning, collaboration, and consideration of various factors. The process should involve key stakeholders, including IT teams, application owners, security experts, and compliance officers, and spans plan development and target architecture design.
Migration plan development
Create the migration plan, taking the following considerations into account:
- Cloud strategy: Determine the desired target cloud architecture based on the IT strategy and a cloud-first approach. Select the appropriate cloud service providers and deployment models (public, private, and/or hybrid).
- Process: Create a clear and detailed plan outlining the steps involved in the migration journey, from pre-migration preparation to post-migration validation.
- Timelines: Establish realistic timelines for each migration step, considering application complexity, data volume, and dependencies. Clearly define milestones and set achievable deadlines to ensure proper coordination and minimize disruptions.
- Resource requirements: Identify the necessary resources for the migration, including personnel, infrastructure, tools, and budget. Allocate resources effectively to ensure a smooth and successful migration.
- Risk mitigation strategies: Anticipate and address potential risks and challenges during migration. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as thorough testing, fallback plans, and efficient communication channels.
Target cloud architecture design
In designing the cloud architecture, consider the following factors to ensure success:
- Scalability: Assess the scalability requirements of applications and design the cloud architecture to accommodate future growth. Utilize cloud-native services and elastic resources to scale applications based on demand.
- Security: Implement robust security measures in the cloud architecture design, including identity and access management controls, encryption mechanisms, and network security configurations, to protect data and applications in the cloud.
- Performance: Analyze the performance requirements of applications and design the cloud architecture accordingly. Optimize performance by considering latency, throughput, and response times using cloud-native services, caching mechanisms, and load-balancing techniques.
- Compliance requirements: Understand and address regulatory or compliance requirements for migrating applications. Ensure that the target cloud architecture meets compliance standards and implements data protection and privacy measures.
Choose the right provider and services
Selecting the right provider and associated services is crucial to cloud migration success. Here are some specific steps to choosing the cloud service provider that will best meet your needs:
- Consider providers’ track records, financial stability, and customer reviews.
- Assess their cloud migration experience and ability to support your workload and technology stack.
- Evaluate their service offerings—including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS)—to determine the best fit for your organization.
- Consider compute resources, storage options, databases, networking, security services, and management tools.
- Assess their compatibility with hybrid or multi-cloud strategies, if applicable.
- Security and compliance are paramount, so ensure that the provider has robust security measures and relevant certifications.
- Evaluate their pricing models, including costs for compute resources, storage, and additional services.
- Review their support and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure that they align with your needs.
Implement robust security measures
When transitioning to the cloud, it’s essential to prioritize the security of your data, applications, and infrastructure, making the implementation of robust security measures a critical cloud migration best practice. This involves a number of key steps:
- Ensure that data encryption is employed both in transit and at rest to safeguard sensitive information.
- Implement strong access controls, authentication mechanisms, and multifactor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Verify every access request, and require explicit permission for each action taken within the cloud environment. This mindset shifts the traditional perimeter-based security model to a more granular and dynamic approach.
- Divide security controls among different teams or individuals. This segregation of duties reduces human errors and helps establish checks and balances.
- Regularly monitor and audit access logs and system activity to detect and respond to potential security incidents.
- Employ network security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) protection to defend against external threats.
- Implement vulnerability management processes to identify and remediate potential security weaknesses.
- Regularly update and patch software to address any known vulnerabilities.
- Implement robust backup and disaster recovery mechanisms to protect against data loss and ensure business continuity.
- Train employees on security best practices to mitigate the risks associated with human error and social engineering attacks.
Optimize applications for the cloud
Organizations can maximize performance, scalability, and cost efficiency by adapting and optimizing applications to take full advantage of cloud capabilities. The following are some key considerations:
- Rearchitect applications to leverage cloud-native services.
- Design applications for elasticity and scalability; leverage auto-scaling features to adjust resources based on demand dynamically.
- Optimize application performance by leveraging content delivery networks (CDNs), caching mechanisms, and data compression techniques. Use distributed caching and in-memory data stores to minimize latency and improve response times.
- Implement robust monitoring and logging mechanisms to gain insights into application performance and identify bottlenecks. Leverage cloud-native monitoring services to collect and analyze metrics, logs, and traces.
- Ensure application resilience and fault tolerance by implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms. Leverage the cloud provider’s load balancers and fault-tolerant architecture patterns to ensure high availability.
- Consider refactoring applications to use serverless computing, eliminating the need to provision and manage servers. Serverless functions allow for event-driven architectures, optimizing resource utilization and cost efficiency.
- Conduct comprehensive testing to ensure application compatibility and performance in the cloud environment.
Assess data migration strategies
Following the right data migration strategies is crucial to ensuring a smooth transition to the cloud. Consider the following approaches:
- Start by thoroughly assessing your data and identifying its volume, complexity, and dependencies. Categorize the data based on sensitivity, compliance requirements, and business importance to prioritize migration efforts.
- Choose an appropriate data migration method, such as direct transfer, backup and restore, or leveraging data transfer services provided by the cloud provider.
- Implement data validation and integrity checks to ensure the accuracy and completeness of migrated data.
- Plan to minimize downtime and establish proper data replication and synchronization mechanisms during migration.
- Consider leveraging data compression, encryption, and deduplication techniques to optimize storage and ensure data security.
- Finally, test the migrated data thoroughly to validate its integrity and functionality in the cloud environment.
By considering these data migration strategies, organizations can successfully move their data to the cloud while minimizing risks and ensuring a seamless transition.
Implement governance and compliance
To meet regulatory requirements in the cloud, organizations should establish strong governance and compliance frameworks:
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clearly define the responsibilities related to access control, data handling, and incident response. Assign appropriate roles to ensure accountability and the proper management of cloud resources.
- Implement identity and access management (IAM): Utilize IAM controls to manage user permissions effectively. Enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary access rights. Regularly review and update user access privileges as needed.
- Monitor and audit user activities: Implement robust monitoring and auditing mechanisms to track user activities in the cloud environment. This helps with promptly detecting any suspicious behavior or policy violations.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations: Understand the specific requirements of relevant industry standards and regulations (such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS) and align cloud practices accordingly. Evaluate the cloud provider’s compliance certifications and security practices to ensure that they meet the necessary standards.
- Establish data retention and deletion policies: Develop policies for data retention and deletion that comply with regulatory requirements. Define how long data should be stored, and establish secure processes for data disposal when it is no longer needed.
- Conduct security assessments and vulnerability scans: Regularly perform security assessments and scans to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in the cloud environment. Address any identified issues promptly to maintain a secure and compliant infrastructure.
- Establish ongoing monitoring and reporting: Set up a framework for continuous monitoring, reporting, and compliance assessment. Regularly review and assess the effectiveness of security controls and compliance measures to ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements.
Test thoroughly
Thorough testing is a vital cloud migration best practice to ensure a successful and seamless transition. It involves conducting comprehensive tests on applications, infrastructure, and data in the cloud environment.
First, perform functional testing to verify that applications and services work as intended; test performance to ensure that the cloud infrastructure can handle the expected workload. Next, validate data integrity and security through rigorous data migration and storage process testing. Finally, conduct scalability and resilience testing to verify that the system can handle a variety of loads and recover from failures.
Thorough testing mitigates risks, identifies potential issues, and ensures that the cloud environment meets the organization’s requirements, delivering a reliable and optimized solution.
Continuously monitor and optimize
Continuously monitoring and optimizing is a crucial practice in cloud migration that ensures your cloud environment’s long-term success and efficiency. This process must span your cloud infrastructure, applications, and services.
Monitoring is essential for maintaining the health and security of your cloud environment:
- Implement comprehensive monitoring solutions to track essential metrics like performance, availability, and security incidents.
- Establish alerts and notifications to let the team quickly address any anomalies or performance bottlenecks that may arise.
- Utilize logging and analytics tools to gain valuable insights and proactively detect issues before they impact users.
- Regularly review and update your security measures to ensure adherence to industry best practices and compliance requirements.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits to identify and address potential risks.
Optimization involves regularly assessing resource utilization, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments. This includes rightsizing instances, optimizing storage, and fine-tuning configurations for optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Continuously refine your architecture by leveraging cloud-native services and automation tools. This helps streamline processes and enhance scalability, allowing you to adapt and scale your cloud environment as needed.
By continuously optimizing and monitoring your cloud environment, you can maintain its efficiency, security, and compliance, ensuring its long-term success.
Final thoughts
It is clear that migrating to the cloud isn’t a one-size-fits-all process—it’s a journey that demands a thorough, holistic strategy. Following a well-structured framework based on best practices can empower organizations to effectively traverse the labyrinth of cloud migration challenges, unlocking new avenues of growth and innovation.
At the heart of a successful cloud migration lie a few fundamental principles: detailed assessment and prioritization of workloads, meticulous planning, strategic selection of cloud providers and services, and stringent security protocols. Additionally, optimizing applications for the cloud, deploying effective data migration strategies, and adhering to governance and compliance standards are all vital.
And the work continues beyond successful migration. Uncovering potential issues through exhaustive testing and continuously optimizing and monitoring the cloud environment is crucial for long-term success and maximizing the value derived from the cloud.
The journey to the cloud is less about the destination and more about ongoing transformation. With a toolset like Device42 that simplifies the process through automated discovery, application dependency mapping, and cloud readiness assessments, organizations can confidently stride towards a future where cloud computing isn’t just a tool but a catalyst for operational transformation and a harbinger of digital innovation.




